User Guide

Welcome to Mass Linkers — a powerful Desktop application tool that helps Computer Science (CS) students find study support from batchmates.
1. About Mass Linkers
Mass Linkers helps you find batchmates to form study groups and seek study advice through the following way.
It provides a centralised platform for you to
- save your batchmates’ contact and module details
- search for batchmates with common interests or who are taking similar modules as you conveniently.
A fast typer? Mass Linkers is made just for you. It is optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of an aesthetic Graphical User Interface (GUI).
2. Using the User Guide
In this User Guide, we will take you through the many useful features and functions of Mass Linkers, and provide you crucial information on how the different commands are used.
Feeling lost as a first-time user? We advise you to follow the User Guide sequentially, starting from Getting started, as it provides a natural flow of how the commands should be executed.
If you are more familiar with CLI or Mass Linkers, head over to the Command summary to start using the app.
The following icons are used in the User Guide to denote special information to look out for.
2.1. Meaning of icons
![]() : Additional information such as specific requirements of parameters and the nature of command
: Additional information such as specific requirements of parameters and the nature of command
3. Table of contents
- 1. About Mass Linkers
- 2. Using the User Guide
- 3. Table of contents
- 4. Getting started
-
5. Features
- 5.1. Batchmate commands
- 5.2. Interest commands
-
5.3. Module commands
- 5.3.1. View a batchmate’s modules
- 5.3.2. Add module to a batchmate:
mod add - 5.3.3. Delete module from a batchmate:
mod delete - 5.3.4. Mark module as taken:
mod mark - 5.3.5. Unmark module as not taken:
mod unmark - 5.3.6. Mark all modules as taken:
mod mark all - 5.3.7. Find batchmates taking specified modules:
mod find - 5.3.8. Find modules taken or taking:
mod find takenormod find taking
- 5.4. General commands
- 5.5. Parameter Requirements
- 5.6. Module Categorisation
- 6. FAQ
- 7. Command summary
4. Getting started
- Ensure you have Java
11or above installed on your computer.- To check for the Java version on your computer, you can first open the command-line or terminal window. Then, run the command
java -version. The output will display the version of the Java package installed on your system. - If you do not have Java
11or above in your computer, head to the Technical Support section for the installation guide.
- To check for the Java version on your computer, you can first open the command-line or terminal window. Then, run the command
-
Download the latest
MassLinkers.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Mass Linkers.
- Double-click the file to start the app. If done correctly, the GUI similar to the one below should appear in a few seconds. The image below is annotated with the various sections of the UI.
- Note for Mac users: If you face difficulty running Mass Linkers, refer to the FAQ section.
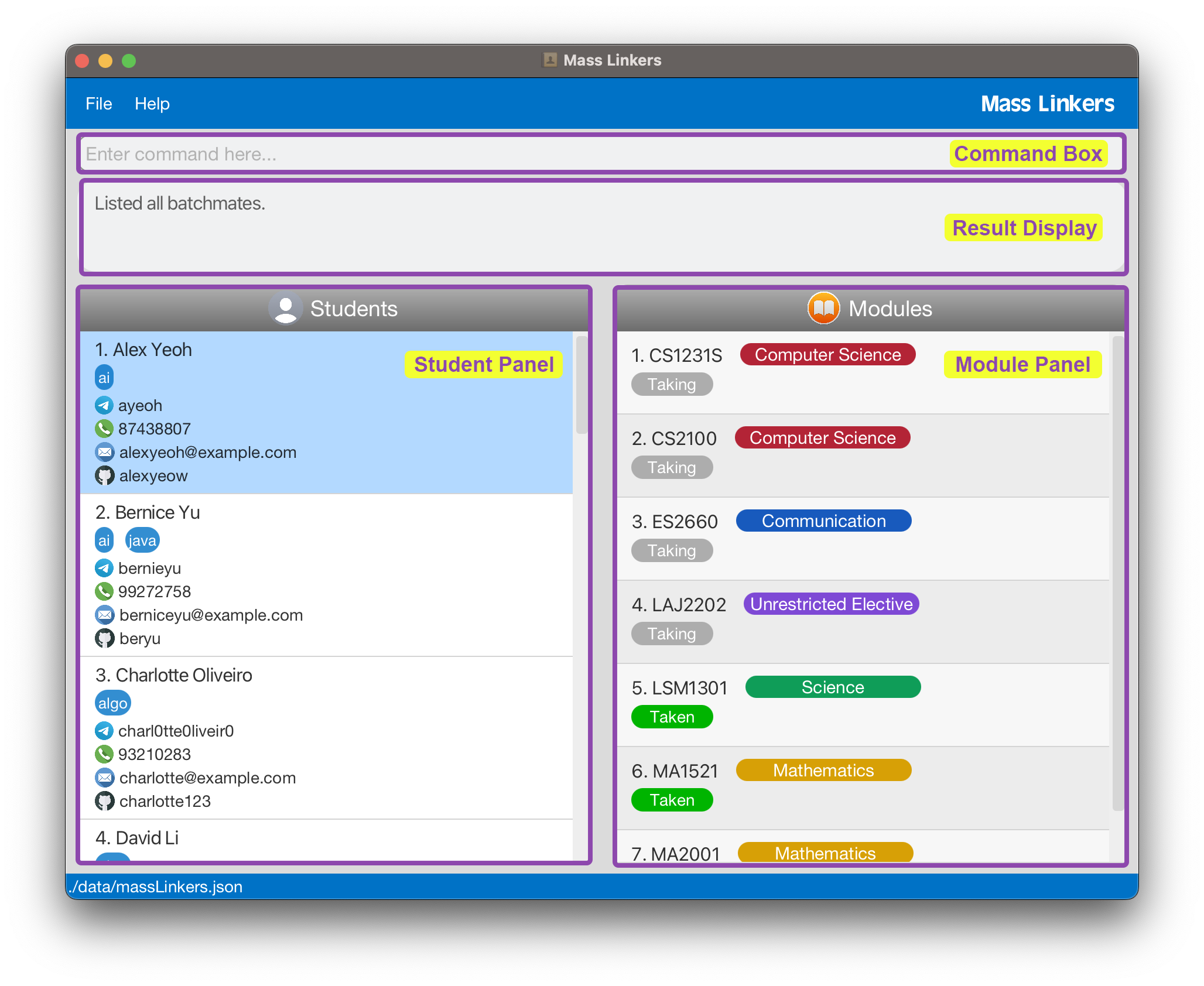
- Note for Mac users: If you face difficulty running Mass Linkers, refer to the FAQ section.
- The app has been populated with some sample data. If you wish to start with an empty set of data, execute the Clear command.
- Type a command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. Refer to the section on Features below for details and usage of each command.
- You can also use the
helpcommand in Mass Linkers to view a summary of all available commands and their syntax.
5. Features
There are 4 main types of commands used in Mass Linkers - Batchmate commands, Interest commands, Module commands and General commands.
By segregating the commands in this manner, this makes it easier to make modifications and conduct a search based on different fields (i.e. search by common interests, modules or personal information).
The following notes outline several noteworthy format that the Features section uses in detailing the usage of different commands.
![]() Take note of the Command Format:
Take note of the Command Format:
- Words in
UPPER_CASEare parameters to be supplied by the user.
Example:- In
add n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe.
- In
- Items in square brackets are optional.
Example:-
n/NAME t/TELEGRAM [i/INTEREST]can be used asn/John Doe t/johnxyz i/aior asn/John Doe t/johnxyzwithout usingi/INTEREST.
-
- Items with
...after them can be used multiple times.
Examples:-
[i/INTEREST]...can be used asi/ai,i/algo i/sweetc.
-
[MORE_MODULES]...can be used ascs2100,cs2103t cs2101 cs2105etc.
-
- Parameters can be in any order.
Example:- If the command specifies
n/NAME t/TELEGRAM [g/GITHUB] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [i/INTEREST], then[i/INTEREST] [e/EMAIL] [p/PHONE] n/NAME [g/GITHUB] t/TELEGRAMis also acceptable.
- If the command specifies
- Any words that come after a prefix will be taken as the parameter.
Example:-
n/john smith t/johnxyz parallelisationjohn parallelization would be considered as the parameter for the telegram handle, which is invalid.
ie. a space does not demarcate the end of a parameter.
-
- If a parameter is expected only once in the command, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
Example:
- If you specify
n/John Doe n/Bob Tan, onlyn/Bob Tanwill be saved. - If you specify
p/12341234p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be saved.
- If you specify
- Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) andmod mark allwill be ignored.
Example:- If the command specifies
help 123, it will be interpreted ashelp. - If the command specifies
exit 345, it will be interpreted asexit. - If the command specifies
mod mark all 123, it will be interpreted asmod mark all.
- If the command specifies
Parameters are the input words that come after a command word to specify how the command should be executed. Click here to view the list of parameter requirements.
![]() Regarding parameters:
Regarding parameters:
- For all commands involving
INDEX,INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the currently displayed list.
-
Beware!!! This may not be the full list of batchmates you have in Mass Linkers! For example, you may have entered the find command, so the currently displayed list will be the result of
findwhich is not the full list. - The index must be a positive integer, e.g. 1, 2, 3 … and be smaller than or equal to the number of batchmates in the currently displayed list.
-
Beware!!! This may not be the full list of batchmates you have in Mass Linkers! For example, you may have entered the find command, so the currently displayed list will be the result of
5.1. Batchmate commands
Batchmate commands handle the management of a batchmate’s personal information such as Name, Telegram, GitHub and Phone number.
5.1.1. Add a batchmate: add
Adds a batchmate to the list of batchmates in the Students panel.
Format: add n/NAME t/TELEGRAM [g/GITHUB] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [i/INTEREST]... [m/MODULE]...
- A summary of the requirements of each parameter can be found under Parameter Requirements.
- Only unique batchmate can be added. It is considered a duplicate if an existing batchmate and the current batchmate to be added have an identical Telegram handle, GitHub username, email address or phone number.
- Modules added to a batchmate will be automatically categorised according to their prefixes. e.g.
cs2103twill be tagged asComputer Science.ma1521will be tagged asMathematics. For modules that are not identified by Mass Linkers, they will be tagged asUnrestricted Elective. More information can be found under Module Categorisation.
Examples:
-
add n/John Doe t/johnxyzadds a batchmate namedJohn Doewith telegram handlejohnxyzto the list. -
add n/John Doe t/johnxyz g/johndoe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com i/ai i/sweadds a batchmate namedJohn Doewith telegram handlejohnxyz, GitHub usernamejohndoe, phone number98765432, email addressjohnd@example.comand interests inaiandsweto the list. -
add n/John Doe t/johnxyz m/cs2103t m/cs2101adds a batchmate namedJohn Doewith telegram handlejohnxyzand modulescs2103tandcs2101to the list.
5.1.2. Edit a batchmate: edit
Edits the information of a specified batchmate in the Students panel.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [t/TELEGRAM] [g/GITHUB] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [i/INTEREST]...
- Edits the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Students panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details. - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing interests, the existing interests of the batchmate will be completely replaced by the new ones.
- You may not change Telegram handle, GitHub username, email address or phone number to one that has already been owned by someone in the Mass Linkers.
i/ without specifying any interests after it.
Examples:
-
edit 1 g/johndoe p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comedits the GitHub username, phone number and email address of the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list to bejohndoe,91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Bob Tan i/edits the name of the 2nd batchmate in the currently displayed list to beBob Tanand clears all existing interests.
5.1.3. Delete a batchmate: delete
Deletes a specified batchmate from the Students panel.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Students panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd batchmate in the full list of batchmates you have in Mass Linkers. -
find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list of thefindcommand.
5.1.4. Find a batchmate: find
Finds batchmates whose details contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]...
-
NAME,TELEGRAM,GITHUB,PHONEandEMAILare searched simultaneously. - The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
jOnAswill returnJonas,ivAnwill returnIvan. - Finding by
NAME:- The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Ming Qingwill return bothMing QingandQing Ming. - Batchmates matching at least one keyword will be returned. e.g.
Ming Xuanwill returnMing Qing,Yu Xuan. - Only full words will be matched. e.g.
Qinwill not return a batchmate with the nameQing. You need to writeQing.
- The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
- Finding by
TELEGRAM,GITHUB,PHONEandEMAIL:- Partial words are accepted. E.g.
uxuwill returnyuxuan. - Unlike
NAME, these items (TELEGRAM,GITHUB,PHONEandEMAIL) are not separated by spaces. If full words are needed for matching, you will have to type the full item out each time you search.
- Partial words are accepted. E.g.
TELEGRAM, GITHUB, PHONE and EMAIL are unique. If your partial text input is too common and list too many batchmates, simply type a few more letters! It is still better than typing the entire item!
![]() find:
find:
find command searches NAME, TELEGRAM, GITHUB, PHONE and EMAIL simultaneously.
Examples:
- When you want to search by
NAME:-
find mingreturnsMing,Ming QingandHong Ming. -
find byron henryreturnsByron Huang,Henry Chuah.
-
- When you want to search by
TELEGRAM,GITHUBorEMAIL:-
find ionreturns the batchmates with Telegram handle, GitHub username or email address containingion, e.g. batchmate with telegram handleliona, batchmate with GitHub usernamethecation47.
-
- When you want to search by
PHONE:-
find 999returns the batchmates with phone numbers69998888,89991234or99912345.
-
5.1.5. List all batchmates: list
Shows a list of all batchmates in the Students panel.
Format: list
5.2. Interest commands
Interest commands manage a batchmate’s list of interests, such as the addition of interests, deletion of interests and searching batchmates with specified interests.
![]() What are considered interests:
What are considered interests:
Interests can include batchmates’ hobbies such as games, CS specialisations, etc.
5.2.1. Add interests: addInt
Adds interest(s) to a specified batchmate in the Students panel.
Format: addInt INDEX INTEREST [MORE_INTERESTS]...
- Adds interest(s) to the batchmate at the specific INDEX in the currently displayed list in the Students panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
- Interests added are case-insensitive and will be displayed in a lower casing.
Examples:
-
addInt 1 algoadds the interestalgoto the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list. -
addInt 3 database swe machinelearningadds the interestsdatabase,sweandmachinelearningto the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list.
5.2.2. Delete interests: deleteInt
Delete interest(s) from a specified batchmate in the Students panel.
Format: deleteInt INDEX INTEREST [MORE_INTERESTS]...
- Deletes interest(s) from the batchmate at the specific INDEX in the currently displayed list in the Students panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
Examples:
-
deleteInt 1 aideletes the interestaifrom the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list. -
deleteInt 3 ai swedeletes the interestsaiandswefrom the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list.
5.2.3. Find batchmates by interests: findInt
Finds batchmates whose interests contain all the specified interests.
Format: findInt INTEREST [MORE_INTERESTS]...
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
machineLearningwill matchmachinelearning. - Only exact words will be matched. e.g.
swwill not matchswe.
Examples:
-
findInt aireturns all batchmates whose interests containai. -
findInt swe securityreturns all batchmates whose interests contain bothsweandsecurity.
5.3. Module commands
Module commands manage a batchmate’s list of modules, such as the addition of modules, deletion of modules and searching batchmates with specified modules.
![]() Note:
Commands used to manage a batchmate’s personal information in Batchmate commands and Interest commands follow the 1 command word syntax. E.g.,
Note:
Commands used to manage a batchmate’s personal information in Batchmate commands and Interest commands follow the 1 command word syntax. E.g., add, addInt.
On the other hand, commands that manage a module detail in Module commands can have multiple command words preceded by the mod keyword. E.g., mod add, mod mark all, mod find taken.
This is to facilitate easy distinction between the nature of commands.
5.3.1. View a batchmate’s modules
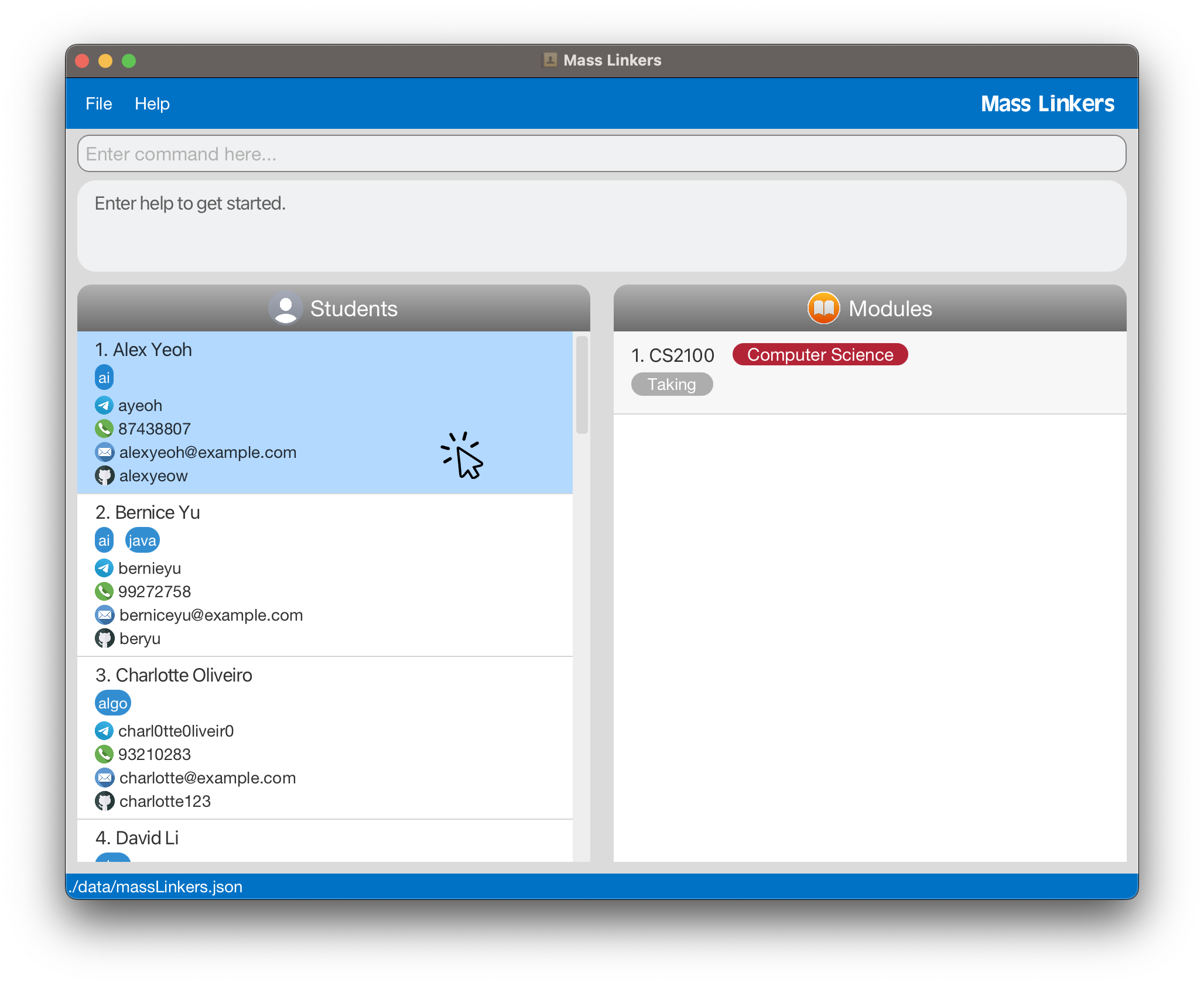
Views the list of modules taken by a batchmate in the Modules panel.
Left-click the row with the batchmate’s name in the Students panel.
- The selected row would turn blue and the Modules panel would display all the modules of the batchmate.
Below is the GUI after you left-click the 1st batchmate in the Students panel. The 1st row turns blue and the Modules panel displays all the modules of the 1st batchmate.
5.3.2. Add module to a batchmate: mod add
Adds module(s) to a specified batchmate in the Modules panel.
Format: mod add INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
- Adds module(s) to the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Modules panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details. - Modules added to a batchmate will be automatically categorised according to their prefixes. e.g.
cs2103twill be tagged asComputer Science.ma1521will be tagged asMathematics. Modules that Mass Linkers cannot identify will be tagged asUnrestricted Elective. More information can be found under Module Categorisation.
Examples:
-
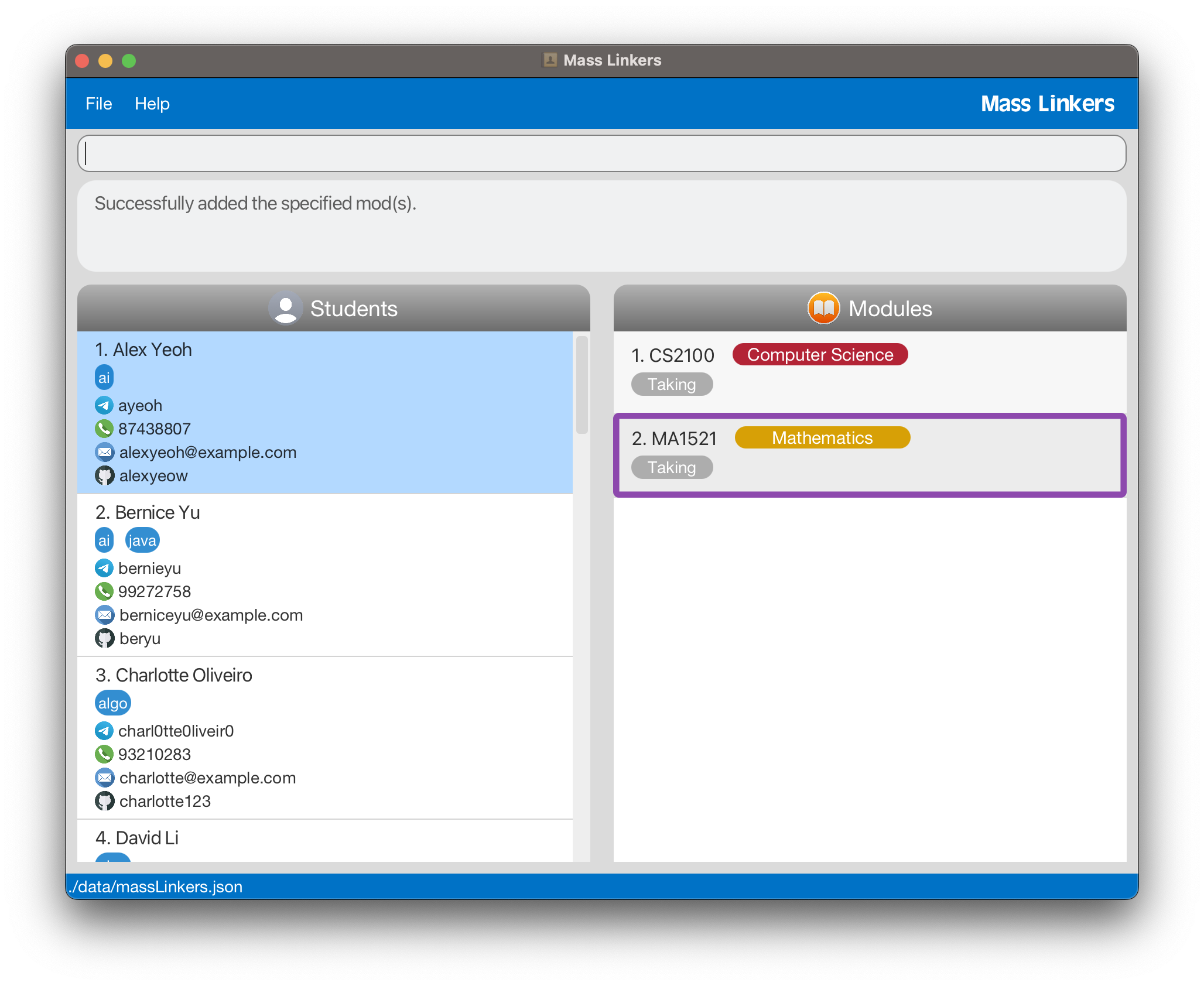
mod add 1 ma1521adds the moduleMA1521to the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list. -
mod add 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105adds the modulesCS2100,CS2103T,CS2101andCS2105to the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list.
Below is the GUI after executing mod add 1 ma1521. The module MA1521 is successfully added to the 1st batchmate and automatically categorised as Mathematics. The expected changes are annotated with a purple rectangular box below.
5.3.3. Delete module from a batchmate: mod delete
Deletes module(s) from a specified batchmate in the Modules panel.
Format: mod delete INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
- Deletes module(s) from the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Modules panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
Examples:
-
mod delete 1 cs2103tdeletes the moduleCS2103Tfrom the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list. -
mod delete 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105deletes the modulesCS2100,CS2103T,CS2101andCS2105from the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list.
mod delete and add the new module using mod add.
5.3.4. Mark module as taken: mod mark
Marks module(s) of a specified batchmate as taken in the Modules panel, which means the batchmate has taken the module(s) before.
Format: mod mark INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
- Marks module(s) of the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Modules panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
Examples:
-
mod mark 1 cs2103tmarks the moduleCS2103Tof the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list astaken. -
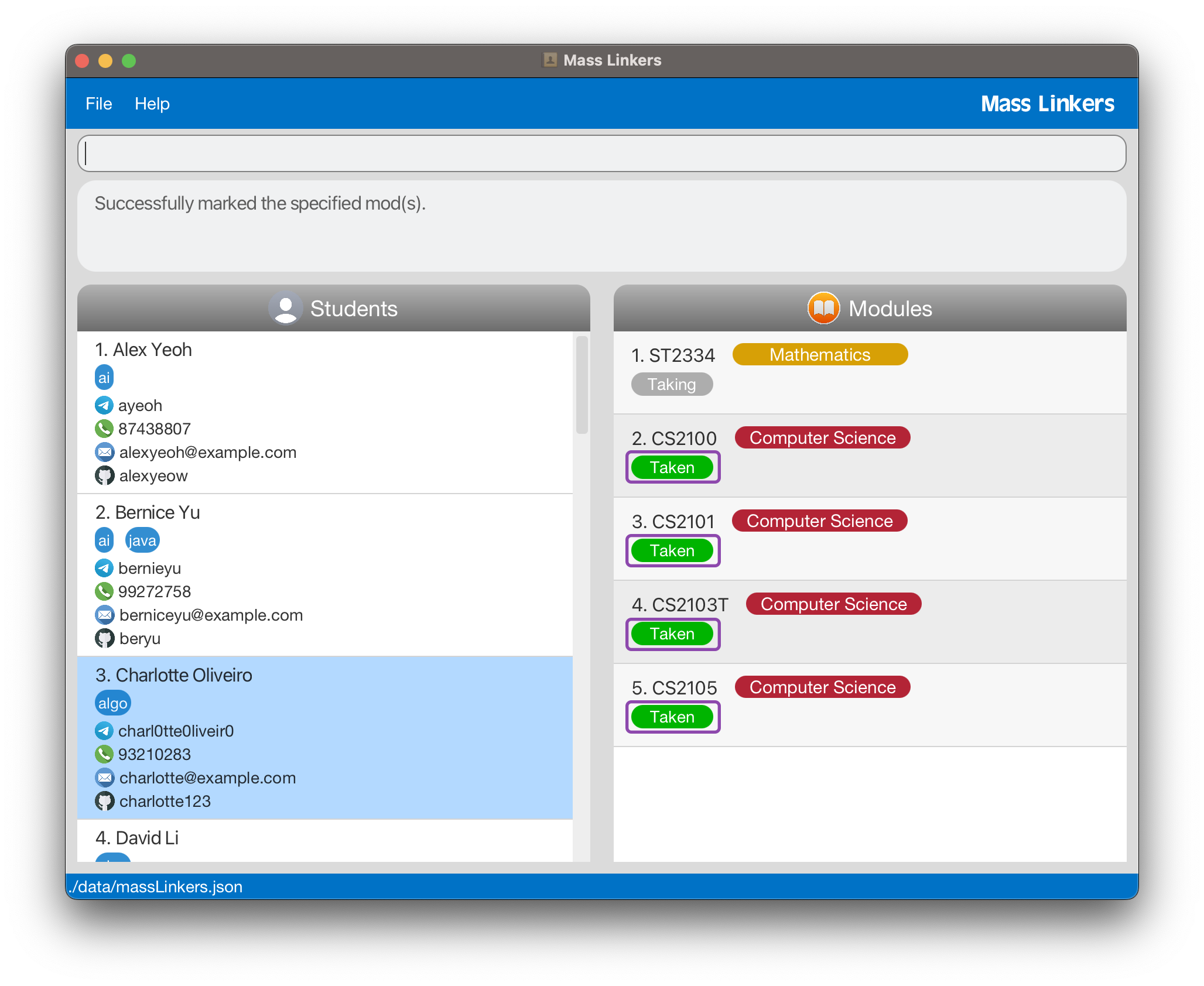
mod mark 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105marks the modulesCS2100,CS2103T,CS2101andCS2105of the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list astaken.
Below is the GUI after executing mod mark 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105. The modules CS2100, CS2103T, CS2101 and CS2105 are successfully marked as taken. The expected changes are annotated with purple rectangular boxes below.
5.3.5. Unmark module as not taken: mod unmark
Unmarks module(s) of a specified batchmate and updates the status as taking in the Modules panel, which means the batchmate is currently taking the module(s).
Format: mod unmark INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
- Unmarks module(s) of the batchmate at the specific
INDEXin the currently displayed list in the Modules panel. Refer to the section on Regarding parameters at the start of Features for more details.
Examples:
-
mod unmark 1 cs2103tunmarks the moduleCS2103Tof the 1st batchmate in the currently displayed list asnot taken. -
mod unmark 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105unmarks the modulesCS2100,CS2103T,CS2101andCS2105of the 3rd batchmate in the currently displayed list asnot taken.
5.3.6. Mark all modules as taken: mod mark all
mod mark all command is irreversible. Only execute it if you intend to mark all existing modules for all batchmates as taken.
Marks all current modules of batchmate currently listed in Mass Linkers as taken in the Modules panel. This makes it convenient to update the module status of all existing modules of every batchmate as taken after each semester.
![]() Note:
To mark all mods present of all students, carry out
Note:
To mark all mods present of all students, carry out list followed by mod mark all.
Format: mod mark all
5.3.7. Find batchmates taking specified modules: mod find
Finds batchmates with modules matching all the specified modules.
Format: mod find MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
cs2100will matchCS2100. - Only full words will be matched. e.g.
cs21will not return batchmates with the modsCS2100andCS2101. - Searching for illegitimate module codes will return 0 student.
Examples:
-
mod find cs2100returns batchmates with the moduleCS2100. -
mod find cs2101 cs2103t cs1231sreturns batchmates with all three modules -CS2101,CS2103TandCS1231S.
5.3.8. Find modules taken or taking: mod find taken or mod find taking
mod find. The rules listed above for mod find apply to this feature too.
Finds batchmates who have taken or are taking all the specified modules.
Format: mod find taken MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... or mod find taking MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
Examples:
-
mod find taken cs2100returns batchmates who have takenCS2100. -
mod find taken cs2101 cs2103t cs1231sreturns batchmates who have taken all three modules -CS2101,CS2103TandCS1231S. -
mod find taking cs2100returns batchmates who are takingCS2100. -
mod find taking cs2101 cs2103t cs1231sreturns batchmates who are taking all three modules -CS2101,CS2103TandCS1231S.
5.4. General commands
General commands are commands which do not fall under any of the above categories.
5.4.1. View help: help
Shows a brief summary of commands with their syntax and a link to the user guide. You can also click the Open User Guide button, which will redirect you to the user guide in your browser.
Format: help
5.4.2. Clear all data: clear
clear command is irreversible. Only execute it if you intend to clear all existing data.
Clears all existing data in Mass Linkers.
Format: clear
5.4.3. Exit the program : exit
Exits Mass Linkers.
Format: exit
5.4.4. Save the data
Mass Linkers ensures your data is saved automatically after executing a command that changes the data. Hence, you do not need to conduct a save manually.
5.5. Parameter Requirements
Below is the summary of requirements to take note of for each parameter for the different commands.
| Parameter | Requirements | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Only alphabetical with spaces allowed. |
Joe, John Doe
|
| Telegram handle | 1. May only contain alphanumeric characters or underscores and have a minimum length of 5 characters. 2. Consecutive and/or starting/ending with underscores are not allowed as per Telegram requirements. |
johndoe, john_doe123
|
| Phone number | 1. Should contain only numerical values (i.e. 0-9), and at most one “+” at the beginning for country code (optional). 2. Should have a length of 7-16 characters (inclusive of country code). 3. Incorrect phone numbers are still accepted, though they are discouraged and a warning will be shown. |
98383913, +12064512559, (+65) 98383913 (Warning will be shown) |
| GitHub username | 1. May only contain alphanumeric characters or hyphens and have a length between 1 - 39 characters. 2. Consecutive and/or starting with hyphens are not allowed as per GitHub requirements. |
john1, john-doe
|
| Interest | Only alphanumerical characters are allowed. |
swe, ai, algo
|
| Emails should be of the format local-part@domain and adhere to the following constraints: 1. The local-part should only contain alphanumeric characters and these special characters within the quotation marks: “ +_.-”. The local-part may not start or end with any special characters.2. This is followed by a ‘@’ and then a domain name. The domain name is made up of domain labels separated by periods. The domain name must: - end with a domain label at least 2 characters long - have each domain label start and end with alphanumeric characters - have each domain label consist of alphanumeric characters, separated only by hyphens, if any. |
john12@gmail.com, joe-lim@u.nus.edu, joe@mail
|
|
| Modules | Module names should be numbers prefixed with alphabets and be less than 10 characters. |
CS2100, CS2103T, ES2660
|
5.6. Module Categorisation
Modules are automatically categorised when you create them. The categorisation is modelled after the prefixes which NUS modules use.
Below is the categorisation:
| Category | Module Prefix |
|---|---|
| Computer Science | CS, IS, CP |
| Mathematics | ST, MA |
| Science | LS, CM, PC |
| General Education | GE, UT |
| Unrestricted Elective | All other prefixes |
Module prefix refers to the first two characters of every module name.
6. FAQ
Facing an issue? Below are several commonly asked questions which address technical and privacy concerns.
6.1. Technical Support
Q: If I do not have Java 11 or above, how can I install it on my computer?
A: Visit this website and follow the installation guide for your operating system.
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install Mass Linkers on the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Mass Linkers home folder.
Q: Do I need an internet connection to use Mass Linkers?
A: No, an internet connection is not required.
Important for Mac users
Q: I am using Mac and I tried opening the MassLinkers.jar file by double-clicking it in Finder. It says “MassLinkers.jar” cannot be opened because it is from an unidentified developer.
A: Right-click the MassLinkers.jar file and select Open. When a warning message that says macOS cannot verify the developer of “MassLinkers.jar”. Are you sure you want to open it? appears, select Open. Alternatively, you can right-click the MassLinkers.jar file and select Open with JavaLauncher(default).
Q: Will the data of batchmates be saved if the program was not closed via the exit command?
A: Yes, the data will still be saved if the program is closed by closing the application window directly. However, we advise using the exit command for a better user experience.
Q: I have accidentally cleared all the data. Is there any way to undo the changes?
A: Currently, there is no undo feature and the clear command is irreversible. Hence, it is extremely important to only use it when you want an empty Student and Module table. However, we are looking into adding undo and redo commands for future developments.
Q: I have added a batchmate whose row exceeds the currently displayed list of batchmates in the Students panel. I have to scroll below to view the newly added batchmate. Is this expected?
A: Yes, adding a new batchmate would not auto-scroll the Students panel to the bottom of the list.
6.2. Privacy Issues
Q: What if I do not want to share some of my personal data like my phone number and email address?
A: While it is every student’s responsibility to exercise discretion in sharing their batchmates’ contacts, Mass Linkers has made more sensitive data fields such as GitHub, Phone and Email optional. In this way, the only mandatory fields are your name and telegram handle. If you are uncomfortable sharing your name, you can use a pseudo-name for identification purposes.
7. Command summary
All the available commands in Mass Linkers are categorised into 4 summary tables below.
7.1. Batchmate commands
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Add | add n/NAME t/TELEGRAM [g/GITHUB] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [i/INTEREST]... [m/MODULE]... |
add n/John Doe t/johnxyz g/johndoe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com i/AI i/swe m/cs2103t m/cs2101 |
| Edit | edit INDEX [n/NAME] [t/TELEGRAM] [g/GITHUB] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [i/INTEREST]... |
edit 1 g/johndoe p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com |
| Delete | delete INDEX |
delete 2 |
| Find | find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]... |
find Alex david |
| List | list |
list |
7.2. Interest commands
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Add interest | addInt INDEX INTEREST [MORE_INTERESTS]... |
addInt 3 algo ai swe |
| Delete interest | deleteInt INDEX INTEREST [MORE_INTERESTS]... |
deleteInt 3 ai swe |
| Find by interest | findInt INTEREST [MORE_INTEREST]... |
findInt ai swe |
7.3. Module commands
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Add module | mod add INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... |
mod add 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105 |
| Delete module | mod delete INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... |
mod delete 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105 |
| Mark module | mod mark INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... |
mod mark 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105 |
| Unmark module | mod unmark INDEX MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... |
mod unmark 3 cs2100 cs2103t cs2101 cs2105 |
| Mark all modules | mod mark all |
mod mark all |
| Find module | mod find MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... |
mod find cs2101 cs2103t |
| Find modules taken or taking |
mod find taken MODULE [MORE_MODULES]... mod find taking MODULE [MORE_MODULES]...
|
mod find taken cs2100 or mod find taking cs2101 cs2103t
|
7.4. General commands
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Help | help |
help |
| Clear all data | clear |
clear |
| Exit | exit |
exit |